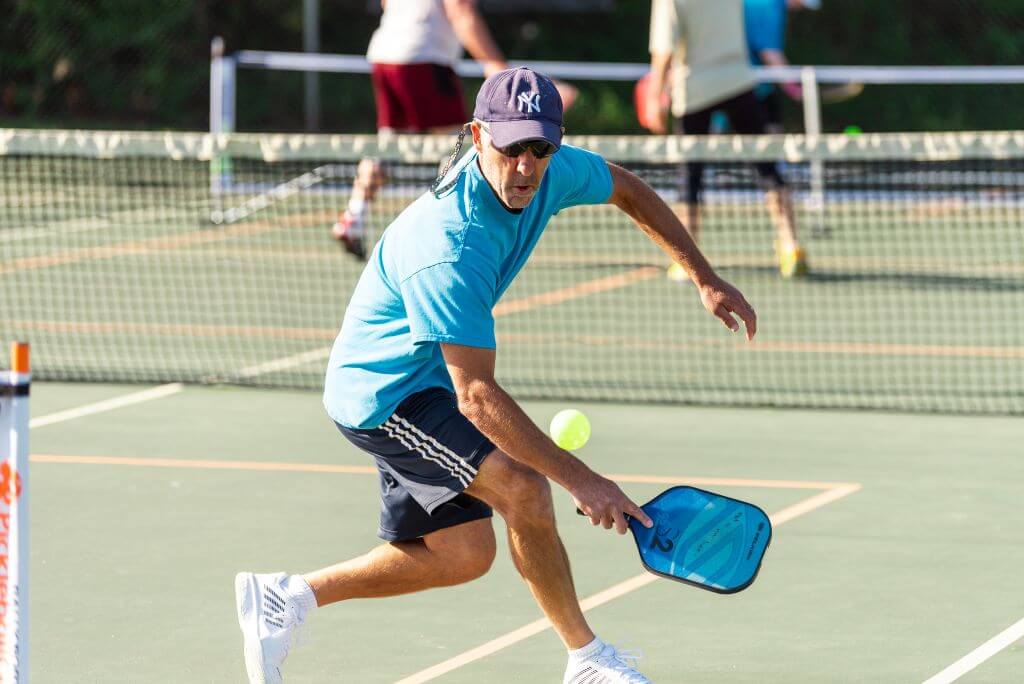
Pickleball started off as a fun, family sport. With a reputation for being a low-impact, friendly game, it was never the kind of sport you would expect to get an injury from. But injuries, like accidents, can happen if you’re not careful.
So, what are the most common pickleball injuries? And what can you do to avoid, prevent, and protect yourself from them?
The Most Common Pickleball Injuries on The Rise
Pickleball is now the fastest-growing sport in America, with a competitive scene that’s only becoming more popular. However, with the rise of the sport and its competitive players, pickleball injuries have also become more and more frequent.
In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common injuries in pickleball, their symptoms, and also how to prevent and treat them.
-
Elbow Injuries
Elbow injuries in pickleball are prevalent due to the repetitive movements done by the arms and wrists. The following are the two most common elbow injuries associated with playing pickleball.
Pickleball Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
If you feel a bit of discomfort on your outer elbow, at the spot where the forearm muscles’ tendons attach to the bone, chances are you have this condition. The pain is caused by microtears in the extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) muscle in the forearm.
| Pickleball Elbow | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | First-line treatments include applying ice, getting plenty of rest, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Counterforce braces can be used to reduce tension on the tendons of the elbow.
But more severe cases may require further medical treatment and physical therapy. Corticosteroid injections can lessen inflammation and reduce the pain in the pickleball elbow in the short term. For long-term relief and better function, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy is recommended. |
| Rehab Time | Most people show improvement within three to six months, but this depends on several factors:
|
| Potential Complication | Complications can include:
Left untreated, pickleball elbow may lead to reduced elbow flexibility caused by the development of scar tissue. Psychological effects like depression or anxiety might also arise. |
Elbow Fracture
The second elbow injury is an elbow fracture. Also, this type of injury results from a break in any of the bones of the elbow—the humerus, radius, and ulna. This usually happens after being hit by a direct, high-impact force, such as falling onto your outstretched arm or being directly hit on the elbow.
| Elbow Fracture | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | The type of treatment for an elbow fracture depends largely on the type, location, and severity of the fracture.
Immobilization with a cast or splint is usually the first-line treatment. But in case of a displaced fracture, where the bones have moved out of alignment, surgical intervention might be necessary. This could involve the use of pins, screws, or plates to hold the bones in place as they heal. After surgery, you’ll need a tailored physical therapy program to restore your elbow’s range of motion, strength, and function. |
| Rehab Time | Although the fracture itself usually mends within about six weeks, you may not regain full function until several months to a year later. This depends on the severity of the fracture, the success of treatment, and commitment to physical therapy. |
| Potential Complication | Beyond persistent pain and stiffness, you might face an increased risk of developing arthritis in the affected elbow.
In severe fractures, there could be damage to the nerves or blood vessels around the elbow. These might lead to problems such as numbness, weakness, or circulatory issues in the arm or hand. Additionally, the improper healing of the fracture, known as malunion, could result in permanent deformity or dysfunction. |
-
Shoulder Injuries
The shoulder joint has a wide range of motion and thus is susceptible to various injuries. The rotator cuff injury is the most common pickleball shoulder injury.
Rotator Cuff Injury
The rotator cuff is a collection of muscles and tendons responsible for shoulder joint stability. These crucial structures can become injured due to repetitive overhead actions like throwing a ball, or a sudden traumatic event like falling on an outstretched arm.
| Rotator Cuff Injury | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | Treatment is multi-faceted, often beginning with rest and ice to alleviate inflammation. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can further assist in reducing pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in treatment, focusing on restoring strength and flexibility to the shoulder. If the injury is severe, surgical intervention may be required, ranging from minimally invasive (arthroscopic surgery) to a full shoulder replacement, depending on the extent of the injury. |
| Rehab Time | The timeline for recovery varies significantly based on the injury’s severity.
|
| Potential Complication | An untreated or improperly managed shoulder injury can lead to chronic shoulder pain and limited range of motion, inhibiting daily activities. Recurrent dislocations of the shoulder may occur.
An injured player may also develop a condition known as “frozen shoulder”, which is characterized by severe stiffness and immobility in the shoulder joint. Another potential complication is “rotator cuff arthropathy”, which is a progressive form of arthritis that develops after a long-standing rotator cuff injury. |
-
Wrist Injury
Repetitive use and high impact can lead to various wrist injuries, from mild sprains to severe fractures.
| Wrist Injury | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | Treatments range from rest and bracing to surgery depending on the severity of the injury. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (or RICE) is a great ways to treat and stabilize wrist injuries on the onset. |
| Rehab Time | Wrist injuries, while mostly minor, require a good three to four weeks minimum to heal. This is because the wrist, even when slightly healed, is one of the most used muscles on and off the pickleball court. |
| Potential Complication | Without the right care and attention, wrist injuries can lead to chronic pain and instability, decreased wrist function, and increased risk of re-injury. |
-
Knee Injuries
Your knees carry your weight and absorb a lot of the force and impact when you run and jump. This is particularly true for sports like pickleball, where you need to be quick on your feet during a rally. This is why the knees are prime targets for injuries. One such common injury is Jumper’s Knee or Patellar Tendonitis.
Jumper’s Knee (Patellar Tendonitis)
An overuse injury, Patellar Tendonitis induces pain in the tendon that serves as a connection between the kneecap (patella) and the shinbone (tibia). This condition is often a consequence of repetitive stress on the knee—particularly from jumping too much—leading to tiny tears in the tendon.
| Jumper’s Knee | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | The RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) protocol is often the first line of treatment to manage pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy that includes stretching and strengthening exercises can also help improve flexibility and build strength around the knee joint, aiding recovery. If conservative treatments are ineffective, corticosteroid injections or Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy could be considered. Surgery is generally the last resort. |
| Rehab Time | The duration of recovery varies widely, typically spanning several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the injury and the individual’s adherence to the treatment plan. |
| Potential Complication | Individuals might experience instability in the knee, increasing the risk of falls. There might even be a recurring cycle of injury if the tendon isn’t given adequate time to heal between injuries.
In the long term, untreated patellar tendonitis can lead to chronic knee pain, which might interfere with daily activities and sports performance. It can cause the tendon to rupture, a condition that requires surgical intervention. |
-
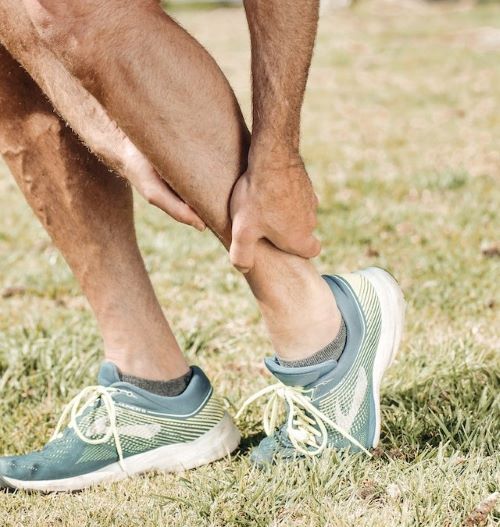
Ankle Injuries
The rapid changes in direction, jumping, and landing involved in sports like pickleball put the ankles at high risk of injury. Thus, common pickleball injuries that involve the ankles include Achilles tendon problems and ankle sprains.
Achilles Tendon Problems
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It is prone to various issues due to overuse, but can also be injured when you suddenly increase your activity levels. Also, these issues may range from inflammation (tendonitis) to microtears (tendinosis) or even complete rupture.
| Achilles Tendon Problems | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | Initial treatment often involves rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications to manage inflammation and discomfort. But stretching and strengthening exercises in physical therapy is crucial to recovery.
If symptoms and pains persist despite using all possible conservative treatments, surgery may be necessary. |
| Rehab Time | The majority of individuals recover within three to six months. But this may extend to a year or more for severe injuries, such as a complete Achilles tendon rupture. |
| Potential Complication | Untreated or recurrent Achilles tendon problems can lead to chronic heel pain and ankle instability. As a result, a complete Achilles tendon rupture could occur, which requires surgical repair. |
Ankle Sprain
An ankle sprain is a common injury that can happen even if you’re not playing. It happens when you suddenly twist, roll, or shift weight from one foot to the other. These movements can cause the ligaments supporting the ankle to stretch and tear, leading to an ankle sprain.
| Ankle Sprain | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms |
|
| Prevention Strategies |
|
| Treatments | The RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is usually the first-line treatment, followed by physical therapy exercises to restore strength, balance, and flexibility.
Bracing or taping the ankle can provide additional support during the recovery process. Pain relievers can also be used to manage discomfort. |
| Rehab Time | The healing time for most ankle sprains ranges between two to six weeks, depending on the severity of the sprain and the individual’s overall health and recovery ability. |
| Potential Complication | Repeated sprains can lead to long-term problems, including ankle instability, arthritis, and also ongoing or chronic ankle pain and discomfort.
In some cases, a sprain may be so severe as to cause damage to the cartilage or underlying bones in the ankle. This can lead to additional complications. |
How Can You Tell if You’re Injured?
While some injuries make their presence known immediately through acute pain or visible signs like swelling or bruising, others may be more subtle and gradual, manifesting as chronic pain or discomfort.
These possible signs of an injury require immediate attention:
- persistent pain
- limited range of motion
- weakness
- instability
- functional impairment
Don’t be complacent even if it only feels uncomfortable, or the pain isn’t that bad. If you think you’ve injured something, preventing further damage should be your first priority. Listen to your body and get early treatment to prevent minor issues from developing into more serious injuries.
What Is the Difference Between Acute and Chronic Injuries?
Understanding the difference between acute and chronic injuries can help you better manage your health and pickleball practice. Then, let’s illustrate this difference with a simple table:
| Acute Injuries | Chronic Injuries | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sudden injuries are caused by a specific impact or traumatic event. | Slow-developing injuries that occur over time. |
| Causes | Falls, collisions, sprains, strains, fractures. | Overuse, inadequate recovery, poor technique or posture. |
| Symptoms | Sudden, severe pain, swelling, inability to move or bear weight on a limb, visible dislocation, or broken bone. | Persistent or recurring pain, stiffness, limited mobility, weakness, and the frequent sensation of ‘giving way’. |
| Treatment | Immediate medical attention, RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), and possible surgery. | Activity modification, physical therapy, strengthening exercises, pain management, and possible surgery. |
| Prevention | Proper warm-up and cool-down, wearing protective gear, playing within skill level, and maintaining a safe playing environment. | Proper technique, regular breaks, cross-training, adequate rest, and recovery. |
Acute injuries occur much faster and can be more painful. But chronic injuries will last a long time if they go untreated—sometimes, even to the point where your body doesn’t recover 100 percent of its strength back.
Taking Care of Pickleball Injuries: Recovery
Recovering from pickleball injuries is multifaceted, focusing on restoring functionality and strength while preventing further damage.
General Principles of Injury Recovery
The process of injury recovery goes beyond treating the injury site; it requires a full-body approach aimed at promoting overall well-being. This means maintaining a balanced diet that’s rich in proteins and antioxidants that aid in tissue repair, staying hydrated, and ensuring quality sleep.
Additionally, a positive mindset and stress management play critical roles in the recovery process. They help boost your body’s natural healing capacity.
Rest and Immobilization
Rest is essential for your body to heal and recover. Then avoid any activity that causes pain and stresses your injury. Depending on the severity of your injury, a period of immobilization may be necessary. This might involve the use of splints, slings, or casts to prevent movement and protect the injury as it heals.
Ice and Heat Therapy
These are both useful for injury management but for different reasons. Therefore ice therapy is most effective immediately after an injury to reduce inflammation and numb pain. Apply an ice pack to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, every 2-3 hours, for the first 24-72 hours.
Heat therapy, on the other hand, can help relax and loosen tissues and stimulate blood flow, boosting your body’s recovery response. It’s most useful for chronic conditions and should be applied for about 15-20 minutes at a time.
Pain Management
Managing pain is important, not just for comfort, but also to enable participation in physical therapy and exercises that aid recovery. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen can help manage mild to moderate pain.
For more severe pain, you’ll have to consult with a healthcare provider for stronger prescription medications. Also, it’s important to follow dosage instructions and to be aware of any potential side effects. If you do experience any side effects, inform your doctor immediately.
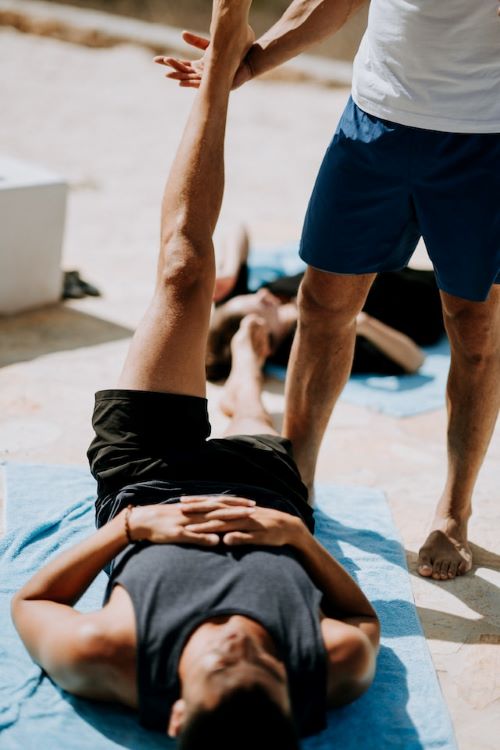
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy is a crucial part of injury recovery. A physical therapist can also design a specific set of exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and balance, thereby promoting recovery and reducing the risk of re-injury. The exercises often start gently and slowly increase in intensity as the injury heals.
Return to Play Slowly
Returning to pickleball after an injury should be a gradual process. Thus, start with light, non-impact activities and slowly increase the intensity as your body allows. Always consult with your healthcare provider or a physical therapist before returning to strenuous physical activities.
Do not rush this process. Returning to play too soon can increase the risk of re-injury.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While minor injuries often heal with self-care, it’s crucial to know when to seek medical attention. It’s always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical advice when in doubt. Signs that you need medical help include:
- severe pain
- inability to move or bear weight on the injured area
- visible deformity
- symptoms not improving with self-care
- symptoms getting worse over time
Avoiding Common Pickleball Injuries: Prevention
The first step to dealing with any problem is to always prevent the problem from happening in the first place. Prevention goes a long way. That’s why it’s one of the most vital preparations that professionals do before playing pickleball or any kind of competitive sport.
Stretching and Warm-Ups
Muscles are like elastic bands. If they’re cold and you try to stretch them too quickly, they’re likely to snap. However, if you’ve warmed them up first, they can stretch further and work more effectively. So, before picking up your paddle, spend about 10-15 minutes on a warm-up routine that includes both general warm-up exercises—like jogging or cycling—and sport-specific drills.
Follow up with stretching exercises, focusing especially on your arms, shoulders, and legs. Stretching your muscles and joints helps improve your range of motion. This prepares your body for the movements it will be performing during the game and reduces the risk of injuries like strains and sprains.
Safety Check for Shoes, Floor, and Grip
Your shoes, the floor you’re playing on, and also your racket grip can all play crucial roles in preventing injuries.
-
Choose Shoes With Good Lateral Support to Protect Your Ankles During Side-To-Side Movements.
The quick and reactive movements required in a pickleball game can put a lot of strain on your ankles and feet. So, it’s crucial to use proper court shoes that provide good grip and ankle support. Also, clean your shoes, especially the soles! You could be wearing high-quality shoes, but if your footwear is dirty, it will be more prone to slipping and sliding.
-
Make Sure the Court Is Clean and Dry to Prevent Slips and Falls.
Always check the court or playing area before any game. Try to look for debris like rocks or leaves or any slippery or uneven areas. These may seem like small hazards, but they are more likely to make your trip and fall.
-
Regularly Check Your Racket Grip as Well—if It’s Worn Out, or Too Large or Small for Your Hand.
Ensure a firm but the comfortable grip on your racket to prevent any wrist strains or chances of developing pickleball elbow. Flying rackets are not uncommon in pickleball, either. Because you could be a hazard to yourself, your teammates, or your opponents.
Proper Recovery of Muscles
Allowing your muscles ample time to recover after a game is just as important as warming them up before. This includes doing cooling-down exercises, which also help gradually lower your heart rate and stretch your muscles. Inadequate muscle recovery time can lead to overuse injuries like tendonitis, which is common in pickleball.
Proper Support for Ankles and Shoes
Ankle injuries are common in pickleball due to the rapid directional changes. To minimize the risk, consider using an ankle brace for additional support, especially if you’ve had an ankle injury before. Choose shoes with good arch support and thick soles that can absorb the impact of quick movements, thus helping to prevent injuries like ankle sprains and Achilles tendonitis.